In today’s digital age, where websites and applications play a pivotal role in shaping our online experiences, user experience (UX) has emerged as a critical factor in determining the success of a digital product.
So What is User Experience?
For example, you want to take your loved ones or anyone in your family or friends to lunch. So what do you prefer? Where do you take them? Does anyone else want to add a restaurant with good reviews, good food reviews, and a pleasing ambiance?
But why do you care? It’s just a lunch, right?
Like, ultimately, you want to go there and have food.

So why are you bothered about the experience? Why are you looking at the reviews if the ambiance is not good? If the experience of the previous person was terrible, we also feel the same because, for lunch, we will have a fun time.
So we want to get a good experience. Here, you might have an idea about what User Experience is.
So it can be your visit to a restaurant, hospital, theme park, airline, or anywhere. So it’s all about the experience that we have, the experience that we get while interacting with that product. So, that is what user experience is all about.
In this blog, we will delve into the fundamental concepts of user experience, its importance, and how it influences the design and performance of modern digital solutions.
Why User Experience Matters?
As a tester, you might get the product towards the end. But then it’s also crucial for you to go back and figure out why the product manager has come up with this layout or has come up with this design. What problem are they trying to solve?
How did they arrive at this? So, all those questions will help you understand the issues of users.
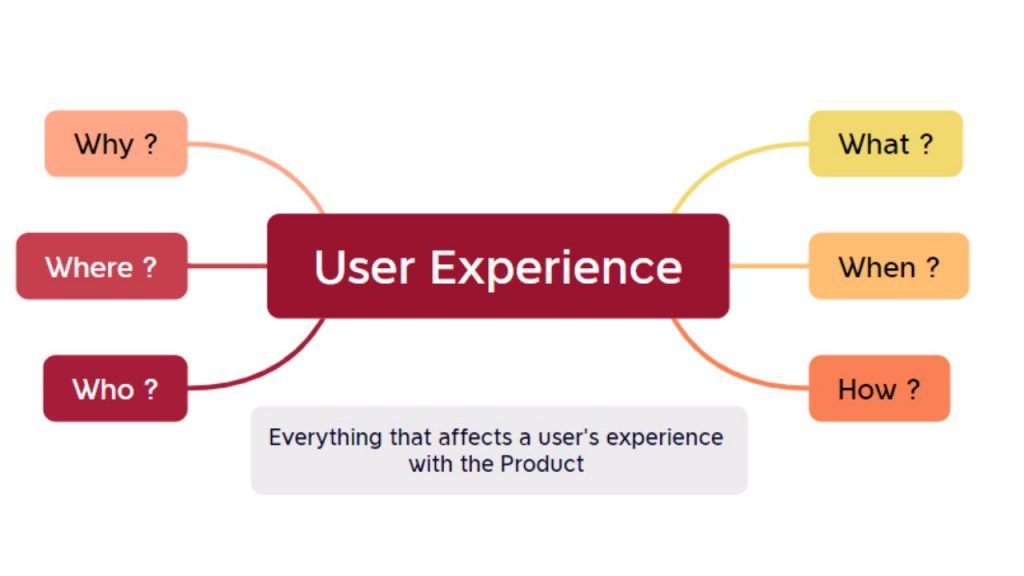
User experience is answering what, when, how, where, and why that affects the user interaction with the product and who will be using your product. So, you mainly concentrate on how your product is being used, when, where, and why the user uses it, and who the target audience is.
Below are some of the reasons why User Experience is essential.
- Customer Satisfaction and Loyalty: A positive user experience leads to higher customer satisfaction, increasing the likelihood of user retention and repeat visits. Satisfied users are more likely to become loyal customers and brand advocates.
- Reduced Bounce Rates: Bounce rate refers to the percentage of users who leave a website after viewing only one page. A well-designed user experience can reduce bounce rates by engaging visitors and encouraging them to explore more pages.
- Higher Conversions: Whether your goal is to sell products, generate leads, or encourage sign-ups, a good user experience can significantly impact conversion rates: clear calls-to-action and intuitive navigation guide users toward desired actions.
- Competitive Advantage: In a crowded digital landscape, businesses prioritizing user experience gain a competitive edge. Users are likelier to choose platforms that offer a smoother and more enjoyable interaction.
- Search Engine Rankings: User experience indirectly influences search engine optimization (SEO). Search engines consider factors like bounce rates, time spent on the site, and mobile-friendliness when ranking websites. A positive UX can lead to improved SEO performance.
What is a Design Flaw?
While talking about the user experience, we will also see some of the flaws or the designs that went wrong where we made the user think about it or confused them about the product’s usage.
—for example, a push and pull door where most of us got it wrong at least once. You pull it When it is pushed, and when it is pulled, you push it.
Why do we go through this?
Why are we using it in the wrong way?
Is it the user’s mistake? Or is the design making us go wrong or confusing us?
These things are called design flaws, which tell us about the learnability of the application.
The Difference Between UI and UX
So we have user experience, and then we talk about UI. These two terms get interchanged often, and we need clarification about what is UX and what is UI. UI is all about the internals of the product. Like, you are talking about the elements, you’re talking about the color, the typography, and the layout;
How should it look? So it’s internal to the product.
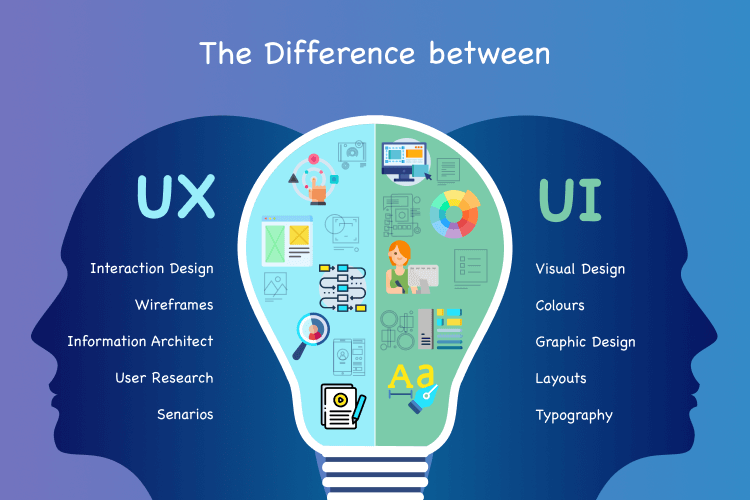
The experience is the outside of the product. So, while using the product, the experience you get, the interactions when you interact with that product. The experience, the smoothness, the smoothness of the application, and the application’s usability are all about the user experience.
The UX Design Process
Creating a remarkable user experience involves a systematic approach:
- Research: Understand your target audience’s needs, preferences, and pain points. Conduct user surveys, interviews, and competitor analysis to gather valuable insights.
- Wireframing: Develop wireframes to outline your digital product’s basic structure and layout. This stage focuses on arranging key elements without getting into visual design details.
- Prototyping: Build interactive prototypes that allow users to navigate through the product. Prototypes help identify potential usability issues and gather user feedback early in the design process.
- Design: Incorporate visual elements into your wireframes and prototypes to create a visually appealing interface. Pay attention to color, typography, and imagery that align with your brand identity.
- Testing: Conduct usability testing with real users to identify any challenges or bottlenecks in the user journey. Iterate and refine your design based on user feedback.
- Implementation: Develop the final product based on the refined design. Collaborate closely with developers to ensure the design is translated accurately into code.
- Monitoring and Iteration: Even after the launch, the UX journey continues. Monitor user interactions, gather feedback, and make iterative improvements to enhance the user experience.
Conclusion
In a digital landscape where user preferences and behaviors are constantly evolving, prioritizing user experience is no longer optional—it’s a necessity. A well-crafted user experience can drive customer satisfaction, boost conversions, and set your digital product apart.
By understanding UX design principles and following a user-centered approach, businesses, and designers can create digital solutions that meet user needs and exceed their expectations.
Remember, a successful digital journey begins with a great user experience.
7